Beneficial Insects for Natural Pest Control in Australian Gardens
A garden filled with Australian native plants.
Creating a healthy garden in Australia often means finding ways to manage pests without relying solely on chemical treatments. One of the most effective and environmentally friendly approaches is encouraging beneficial insects. These natural predators and pollinators not only reduce pest populations but also support biodiversity and soil health. By learning which insects are allies and how to attract them, gardeners can establish long-term, sustainable pest control.
Why Beneficial Insects Matter
Beneficial insects play a crucial role in integrated pest management (IPM). Rather than eliminating all insect life, they help balance populations. Predatory species reduce numbers of destructive pests such as aphids, caterpillars, and mites, while pollinators enhance fruit and vegetable yields. Unlike broad-spectrum insecticides, which can harm non-target species, encouraging beneficial insects preserves ecological diversity and reduces reliance on repeated chemical sprays.
In Australia, many native beneficial insects have co-evolved with our unique plants and climate. Supporting them not only helps with pest control but also contributes to broader conservation goals.
Key Beneficial Insects in Australian Gardens
Lady Beetles (Coccinellidae family)
Lady beetles, also known as ladybirds, are among the most recognizable beneficial insects. Both larvae and adults feed voraciously on aphids, mealybugs, and scale insects¹ ². The common spotted ladybird (Harmonia conformis) is native to Australia and particularly effective at controlling aphid outbreaks. Encouraging lady beetles can significantly reduce the need for chemical aphid sprays.
Lady Beetles (Coccinellidae family)
gardenia.net
Lacewings (Chrysopidae family)
Green lacewings (Mallada signata) are delicate insects whose larvae are nicknamed “aphid lions” due to their aggressive feeding on soft-bodied pests. They consume aphids, whiteflies, thrips, and caterpillar eggs¹ ². Adult lacewings also act as pollinators by feeding on nectar and pollen, making them doubly beneficial.
Lacewings (Chrysopidae family). Green Lacewings, a beneficial insect that devours aphids
Happy Gardener
Hoverflies (Syrphidae family)
Hoverflies, often mistaken for small bees, are vital pollinators and pest controllers. Their larvae consume aphids, scale, and mites, while adults pollinate a wide range of flowers¹. The common hoverfly (Melangyna viridiceps) is frequently seen in Australian gardens. Attracting hoverflies can greatly increase pollination rates while keeping aphids under control.
Hoverflies - Syrphid Fly, Flower Fly, Family Syrphidae.
gardenia.net
Parasitic Wasps (Various families: Braconidae, Ichneumonidae, Trichogrammatidae)
Tiny parasitic wasps lay their eggs inside or on pests such as caterpillars, aphids, and whiteflies. The larvae then consume the host, reducing pest survival. Species like
Trichogramma pretiosum are widely used in horticulture to manage caterpillar infestations.⁴ ² Unlike nuisance wasps, these insects rarely sting humans and focus entirely on pest control.
Heterodontonyx bicolor (orange spider wasp) is a large, strikingly coloured spider wasp from Australia. Brian Jenkins
Predatory Beetles (Carabidae family)
Ground beetles (Pterostichus spp. and others) are nocturnal predators that feed on slugs, caterpillars, and root maggots.² ¹ By sheltering in mulch and leaf litter, they provide natural control at soil level. Their presence is especially valuable in vegetable gardens where soil-borne pests thrive.
Pterostichus madidus, the Pterostichus ovale or Feronia ovale, is a species of beetle insects in the Carabidae family.
entomart.be
Spiders (Order Araneae)
Although technically not insects, spiders are highly effective natural pest controllers. Garden spiders such as the golden orb-weaver (Trichonephila plumipes) capture moths, flies, and even small grasshoppers in their webs.¹ Far from being harmful, most Australian garden spiders are non-dangerous and crucial for pest regulation.
Golden silk orb-weaver - genus of arachnids.
wikidata.org
Tachinid Flies (Tachinidae family)
These parasitic flies resemble houseflies but play a unique role in pest suppression. Female tachinid flies lay eggs on caterpillars, grasshoppers, or beetle larvae. When the eggs hatch, the maggots consume the host. Species like
Trichopoda giacomellii, introduced for biological control, help manage crop-damaging bugs.¹
Scheme of the life cycle of Exorista larvarum.
Maria Luisa Dindo
Native Bees (Tetragonula carbonaria and others)
While not predators, native stingless bees are critical pollinators for many fruit and vegetable crops. By enhancing pollination efficiency, they indirectly reduce the impact of pests on plant productivity. Their role in sustainable food production is increasingly recognised in both commercial and home gardens.¹
Native Australian stingless bees are only 4 mm long. Photo by Erica Siegel.
aussiebee.com.au
Praying Mantises (Mantodea order, e.g., Archimantis latistyla)
Praying mantises are ambush predators that feed on a wide range of garden pests including moths, caterpillars, crickets, grasshoppers, and flies. The Australian stick mantis (Archimantis latistyla) is a common native species.¹ While they may occasionally prey on other beneficial insects, their role as top-level predators makes them valuable allies in pest control.
''Archimantis latistyla'', commonly known as the large brown mantis is a species of mantid native to Australia.
jungledragon.com
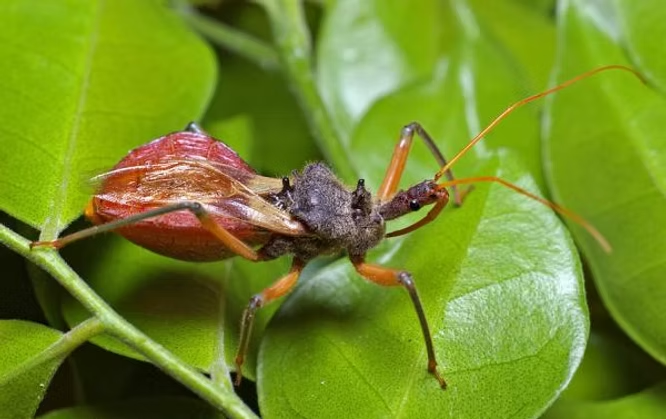
Assassin Bugs (Reduviidae family, e.g., Pristhesancus plagipennis)
Assassin bugs are stealthy hunters that pierce and consume caterpillars, beetles, and other destructive insects. The common assassin bug (Pristhesancus plagipennis) is widespread in eastern Australia and is particularly effective at reducing caterpillar infestations in vegetable gardens.¹ With their sharp proboscis, they inject digestive enzymes into prey, quickly subduing even larger pests.
Adult Assassin Bug - ozwildlife
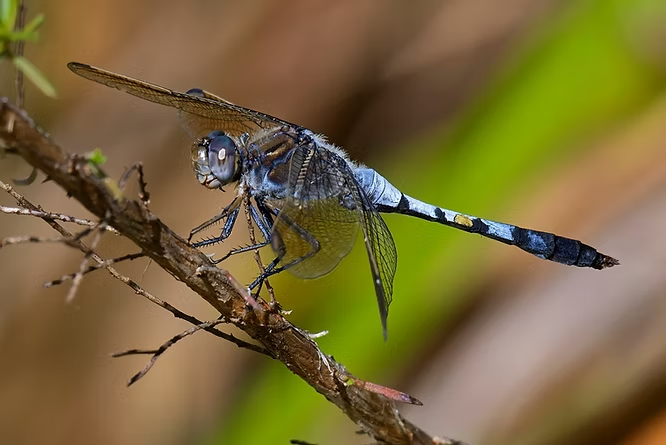
Dragonflies (Odonata: Anisoptera – e.g., Hemianax/Anax papuensis “Australian emperor”, Orthetrum caledonicum “blue skimmer”)
Dragonflies are powerhouse predators at two life stages: aquatic nymphs that ambush mosquito larvae in ponds and rainwater features, and aerial adults that snap up mosquitoes, midges, and small flies on the wing.⁶ ⁷ ⁸ ⁹ ¹⁰ In Australia, the Australian emperor (Hemianax/Anax papuensis) is widespread and highly mobile, while the blue skimmer (Orthetrum caledonicum) is common around still or slow-moving water. Encouraging dragonflies supports a self-replenishing, chemical‑sparing check on nuisance insects in summer months.
Blue Skimmer - Orthetrum caledonicum.
inaturalist.org
How they help: Meta‑analysis across experimental studies shows dragonflies and damselflies can materially reduce mosquito larvae, with strong predation across
Aedes,
Culex and
Anopheles species.¹ Field and lab work in tropical urban settings and Southeast Asia likewise finds odonate nymphs are effective biocontrols—especially where shallow, vegetated breeding habitats are present. While dragonflies aren’t a silver bullet in every landscape, increasing habitat typically boosts their local impact on biting pest pressure.
How to Attract and Support Beneficial Insects
Australian Native Gardens - Cottage garden (Rosella Rise Native Garden).
- Plant Diverse Flowers – Nectar and pollen support adult stages of lacewings, hoverflies, and parasitic wasps. Native flowering plants are particularly effective.
- Provide Shelter – Mulch, leaf litter, and insect hotels create habitat for ground beetles, spiders, mantises, and solitary native bees.
- Avoid Pesticides – Limit home DIY use; this can harm beneficial insects as much as pests. If necessary, contact a licensed professional for tailored recommendations.
- Use Alternatives – Only use things like natural extracts, Eco-Oil, Neem Oil, or White Oil on food plants.
- Predatory insects sold in packs (ladybugs, lacewings, Praying Mantis) – Sometimes available seasonally through garden online specialist stores.
- Incorporate Companion Planting – Herbs like dill, fennel, and coriander attract hoverflies and parasitic wasps, while marigolds deter nematodes and support pollinators.
- Create or keep clean water features (ponds, barrels with mesh, lined troughs) with some
emergent vegetation for nymph cover and adult perches.
- Add
sun‑exposed edges and flat rocks or stakes for basking and hunting posts; emperors patrol open water while skimmers like reeds.
- Reduce excess nutrients (algae blooms) and ensure
some flow or periodic refresh to avoid stagnant water.
The Role of Beneficial Insects in Australian Pest Management
Australia’s climate and biodiversity present unique opportunities for natural pest control. Farmers and gardeners increasingly rely on beneficial insects as part of an Integrated Pest Management (IPM) approach, reducing pesticide resistance and protecting ecosystems.
For home gardeners, the lesson is clear: encouraging beneficial insects is a long-term investment.
While chemical sprays provide short-term relief, they often disrupt natural balances. In contrast, fostering insect biodiversity ensures pests are controlled season after season.
| Beneficial Insect | Scientific Name / Group | Main Prey Controlled | Benefit To Garden |
|---|---|---|---|
| Large Spotted Ladybug | Harmonia conformis (Coccinellidae) | Aphids, mealybugs, scale insects | Rapid reduction of soft-bodied pests |
| Lacewings | Mallada signata (Chrysopidae) | Aphids, whiteflies, thrips, caterpillar eggs | Dual role: predator and pollinator |
| Hoverflies | Melangyna viridiceps (Syrphidae) | Aphids, mites, scale (larvae) | Pollination and aphid control |
| Parasitic Wasps | Trichogramma pretiosum, other Braconidae | Caterpillars, whiteflies, aphids | Biological control of crop pests |
| Predatory Beetles | Pterostichus spp. (Carabidae) | Slugs, caterpillars, root maggots | Soil-level pest suppression |
| Spiders | Trichonephila plumipes (Araneae) | Moths, flies, grasshoppers | Natural top predator, wide prey range |
| Tachinid Flies | Trichopoda giacomellii (Tachinidae) | Caterpillars, grasshoppers, beetle larvae | Strong biological control agent |
| Native Bees | Tetragonula carbonaria and others | Not predators – pollinators | Improved crop yields and fruit set |
| Praying Mantises | Archimantis latistyla (Mantodea) | Caterpillars, grasshoppers, moths, flies | Versatile predator, controls large pests |
| Assassin Bugs | Pristhesancus plagipennis (Reduviidae) | Caterpillars, beetles, other insects | Reduces caterpillar infestations |
| Dragon Flies | Odonata: Anisoptera – e.g., Hemianax/Anax papuensis | Mosquito larvae | Less mosquito bites |
Conclusion
Beneficial insects are essential allies for natural pest control in Australian gardens. From lady beetles and lacewings to praying mantises and assassin bugs, each species plays a role in maintaining ecological balance. By designing gardens that welcome these helpers, Australians can enjoy healthier plants, improved pollination, and reduced reliance on chemicals. Supporting beneficial insects is not just good gardening practice—it is a step toward sustainable living and environmental protection.
Need more advice? contact us for more info
References
- Thia, J. A., & Moreau, J. (2021). Biodiversity and ecosystem services: The role of beneficial insects in sustainable agriculture. Ecological Indicators, 132, 108310.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2021.108310
- Horne, P. A., Page, J., & Nicholson, C. (2020). Practical application of integrated pest management in Australian field crops. Crop Protection, 135, 105201.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cropro.2020.105201
- Gurr, G. M., Wratten, S. D., Tena, A., Hemerik, L., & Heimpel, G. E. (2017). Conservation biological control of pests in the molecular era: New opportunities to address old constraints. Biological Control, 104, 1–4.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biocontrol.2016.10.002
- Furlong, M. J., Zalucki, M. P., & Zalucki, J. M. (2018). Climate change and biological control: The consequences of increasing temperatures on host–parasitoid interactions. Current Opinion in Insect Science, 29, 39–44.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cois.2018.06.006
- Lowe, S., Browne, M., Boudjelas, S., & De Poorter, M. (2019).
100 of the World’s Worst Invasive Alien Species – Including Impacts in Australia. Invasive Species Specialist Group (IUCN).
- Priyadarshana, T. S., & Slade, E. M. (2023). A meta-analysis reveals that dragonflies and damselflies can provide effective biological control of mosquitoes. Journal of Animal Ecology, 92(8), 1589–1600.
https://doi.org/10.1111/1365-2656.13965
- Ramlee, S., et al. (2022).
Odonata nymphs as potential biocontrol agents of mosquito larvae. Southeast Asian Journal of Tropical Medicine and Public Health, 53(4), 426–435. (UM Research Repository)
- Suárez-Tovar, E., Rocha-Ortega, M., Juen, L., & Córdoba-Aguilar, A. (2023). From the forest to the city: the persistence of dragonflies and damselflies in urban environments. Biodiversity and Conservation, 32, 3367–3390. (SpringerLink)
- Australian Museum. (Updated 26 Jul 2024).
Australian Emperor (Anax/Hemianax papuensis)—species factsheet. (ID, habitat and natural history.)
- Atlas of Living Australia. Orthetrum caledonicum (Blue skimmer) species record—distribution and occurrence data for Australia. (Biodiversity Information Exchange)
- Dindo, Maria & Nakamura, Satoshi. (2018).
Oviposition Strategies of Tachinid Parasitoids: Two Exorista Species as Case Studies. International Journal of Insect Science. 10. 117954331875749. 10.1177/1179543318757491.